Students studying information modeling and specification can benefit from homework help in programming complex entity-relationship diagrams and database schema. Tutors providing homework help in programming information systems emphasize proper data normalization, integrity constraints, and relationships between entities to transform requirements into accurate models.
Problem #1
a) In the first population, one element from B corresponds to at most one element from A. Therefore, there is one-to-many relationship. One-to-may constraint should be added.
b) Here, more than one elements from A correspond to more than one elements from B, and vice versa. This is a many-to-many relationship. Many-to-many constraint should be added.
c) In this population, one element from A corresponds to one element from B, and vice versa. This is a one-to-one relationship. One-to-one constraint should be added.
d) Finally, in the last population, at most one element from B corresponds to one or more elements in A. Therefore, this is a many-to-one relationship. Many-to-one constraint should be added.
Problem #2
1)For one-to-many, we can propose the following schema
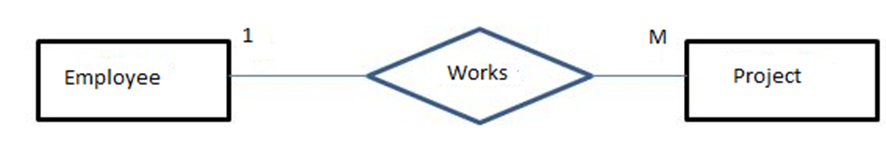
An example of population can be like this:
| E1 | P1 |
| E2 | P2 |
| E1 | P3 |
2) For many-to-one constraint pattern, the scheme is:
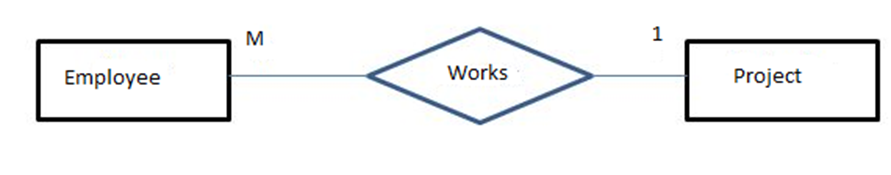
The population can be represented as follows:
| E1 | P1 |
| E2 | P2 |
| E3 | P1 |
3) Scheme:
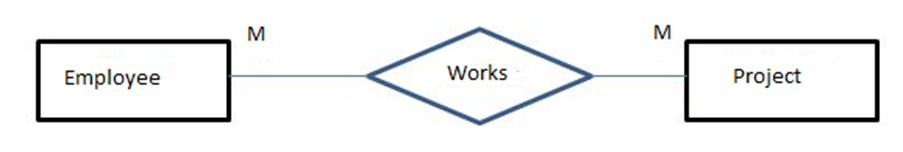
Population:
| E1 | P1 |
| E1 | P2 |
| E2 | P1 |
4) Scheme:
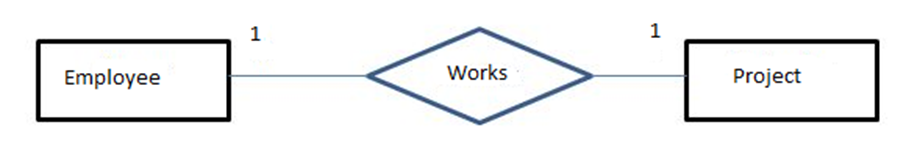
Population:
| E1 | P1 |
| E2 | P2 |
| E3 | P3 |